Introduction
Definition of Warts
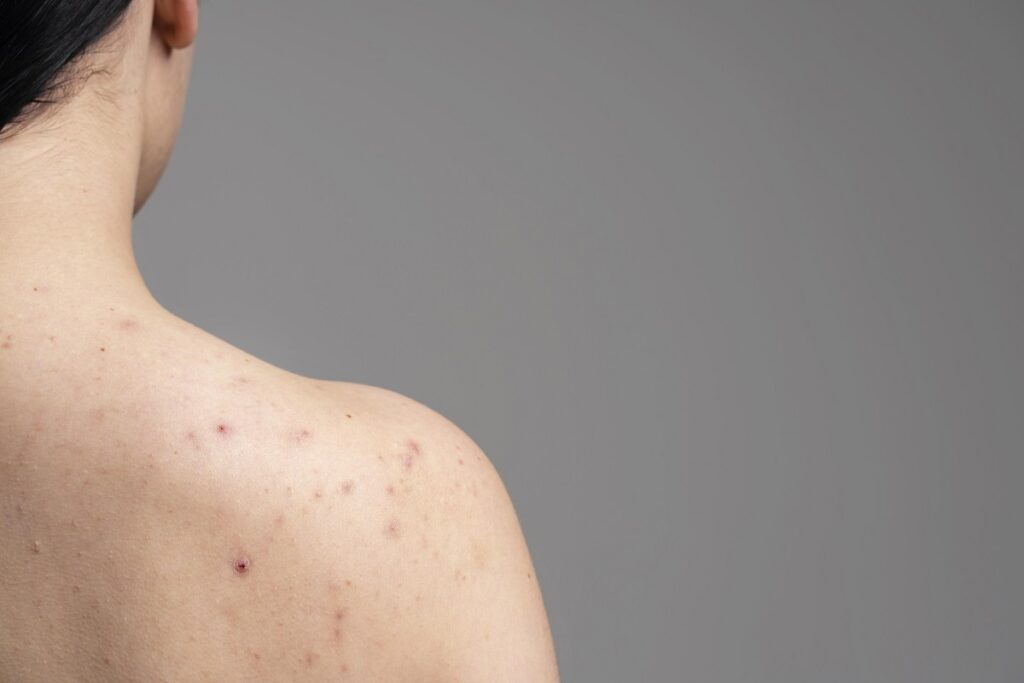
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size, shape, and color. Understanding How to Identify Warts on Your Skin? and what warts are is the first step in identifying and treating them.
Importance of Identifying Warts
Early identification of warts is crucial for effective treatment and preventing their spread. Warts can be unsightly, uncomfortable, and contagious, making timely diagnosis essential for both personal health and the health of others.
Overview of the Guide
This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed information on how to identify warts, including their types, symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, treatment options, preventive measures, and expert insights. Whether you’re experiencing warts yourself or want to learn more about them, this guide covers everything you need to know.
Types and Categories
Common Warts
Common warts, also known as verruca vulgaris, typically appear on the hands and fingers. They are rough, raised bumps with a grainy texture and can have a cauliflower-like appearance. These warts are usually grayish-brown and may have tiny black dots, which are clotted blood vessels.
Plantar Warts
Plantar warts occur on the soles of the feet and can be particularly painful due to the pressure of walking. These warts are often flat due to pressure and can form clusters known as mosaic warts. They may appear as small, rough growths with a well-defined border.
Flat Warts
Flat warts, or verruca plana, are smaller and smoother than other types of warts. They often appear on the face, neck, hands, wrists, and knees. These warts are usually flesh-colored or slightly brown and tend to grow in large numbers.
Filiform Warts
Filiform warts are long, narrow growths that typically appear on the face, particularly around the mouth, eyes, and nose. They can be flesh-colored and have a thread-like appearance, making them easily distinguishable from other types of warts.
Periungual Warts
Periungual warts develop around or under the fingernails and toenails. They can affect nail growth and are often painful. These warts start small but can grow to interfere with nail structure, making them particularly bothersome.
Genital Warts
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain strains of HPV. They appear as small, flesh-colored bumps on the genital or anal area and can cluster together. These warts require medical treatment due to their location and potential complications.
Symptoms and Signs
Physical Appearance
Warts can vary significantly in appearance. Common features include rough, raised surfaces; flat, smooth areas; and thread-like projections. The presence of tiny black dots, which are thrombosed capillaries, is a characteristic sign of common warts.
Common Locations
Warts can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the hands, feet, face, and genitals. The location of a wart can help in identifying its type and the best treatment method.
Pain and Discomfort
While most warts are painless, plantar warts can cause significant discomfort due to their location on the feet. Periungual warts can also be painful as they interfere with nail growth and cause tenderness around the nails.
Variations by Type
Different types of warts have distinct characteristics:
- Common warts: Rough and grainy
- Plantar warts: Flat and painful
- Flat warts: Smooth and numerous
- Filiform warts: Long and thread-like
- Periungual warts: Affect nail growth
- Genital warts: Clustered and flesh-colored
Causes and Risk Factors
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Overview
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a group of more than 100 related viruses. Different types of HPV are responsible for different types of warts. The virus infects the top layer of skin, causing rapid growth of cells on the outer layer.
Transmission Methods
HPV spreads through direct contact with a wart or something that touched a wart, such as towels or personal items. The virus can also enter the skin through small cuts or abrasions, making it easy to contract in communal areas like showers and locker rooms.
Risk Factors
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to HPV infections.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, and other skin injuries provide entry points for the virus.
- Personal Habits: Biting nails or picking at existing warts can spread the virus to other parts of the body.
Diagnosis and Tests
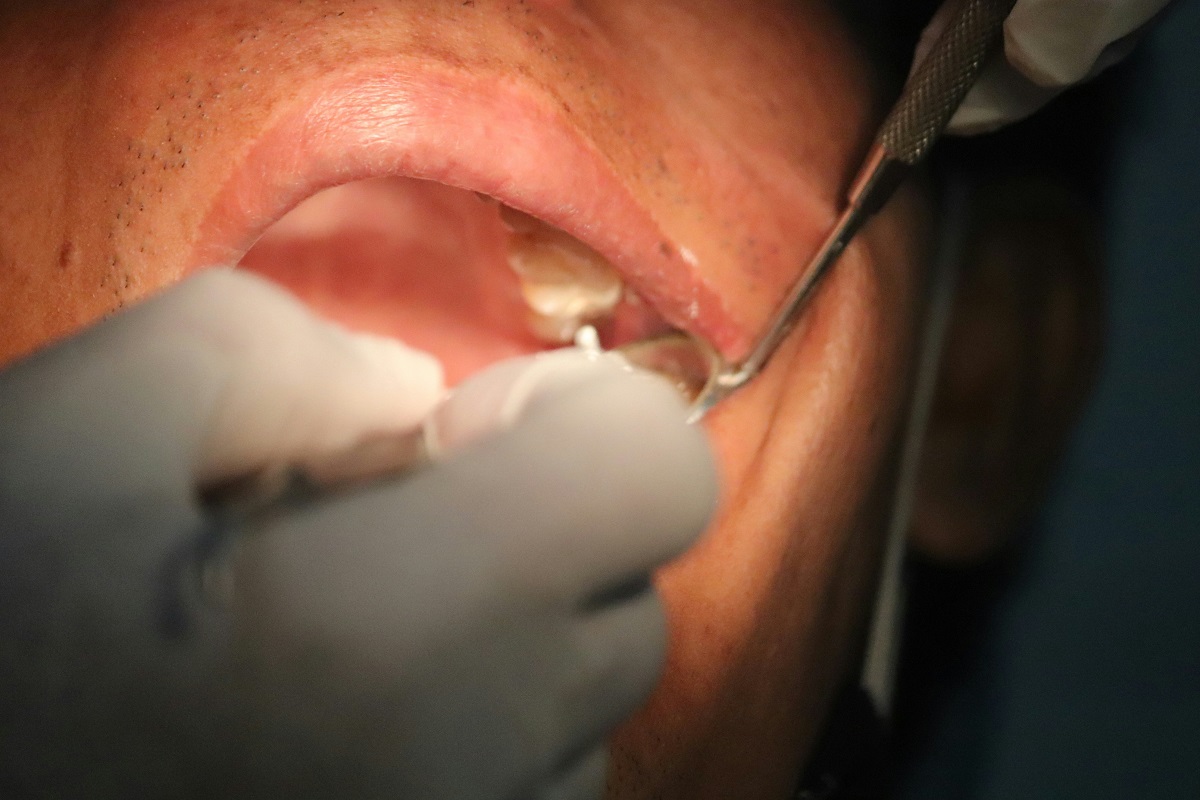
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider can often diagnose warts based on their appearance. The texture, size, and location of the wart are key indicators in identifying the type.
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy involves using a specialized magnifying tool to examine the skin. This tool helps in viewing the wart’s surface in detail, making it easier to differentiate from other skin conditions.
Biopsy
In uncertain cases, a small sample of the wart may be removed and examined under a microscope. This procedure helps confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions, such as skin cancer.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating warts from other skin conditions like corns, calluses, and skin tags is essential for proper treatment. Each condition has unique characteristics that can be identified through careful examination and diagnostic tests.
Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Treatments
- Salicylic Acid: This common treatment works by peeling away the infected skin over time. Available in various forms like gels, pads, and drops, it requires consistent application.
- Cryotherapy Kits: These kits allow for home freezing of warts, similar to the method used by doctors but less potent.
Prescription Medications
For stubborn warts, doctors may prescribe stronger treatments like:
- Cantharidin: A chemical that causes the wart to blister and peel off.
- Imiquimod: A cream that stimulates the immune system to fight the wart virus.
- Bleomycin: An injection that kills the virus directly.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. This method causes the wart to fall off after several treatments and is typically performed by a healthcare provider.
Electrosurgery
Electrosurgery uses an electric current to burn off the wart. This method is often combined with curettage, where the wart is scraped off with a sharp tool.
Laser Treatment
Laser treatment uses intense light to destroy wart tissue. This option is usually reserved for stubborn warts that have not responded to other treatments.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy involves stimulating the immune system to fight the wart virus. Treatments include injections of antigens or topical medications that cause an immune reaction in the wart area.
Home Remedies
Some individuals prefer natural treatments, such as:
- Duct Tape: Covering the wart with duct tape to suffocate it.
- Garlic: Applying crushed garlic to the wart.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Soaking a cotton ball in vinegar and applying it to the wart.
Preventive Measures
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene can help prevent the spread of warts. Regular hand washing, keeping feet dry, and avoiding sharing personal items are essential practices.
Avoiding Contact with Warts
Refrain from touching warts on yourself or others. Use protective barriers, like gloves or bandages, if contact is unavoidable.
Strengthening the Immune System
A healthy immune system can help fight off HPV infections. Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly are ways to boost your immunity.
Protective Measures in Public Places
Wearing flip-flops in communal showers, avoiding walking barefoot in public areas, and using clean, dry towels can reduce the risk of contracting warts in public places.
Personal Stories or Case Studies
Real-Life Experiences
Sharing stories from individuals who have dealt with warts can provide valuable insights and hope. These accounts highlight the emotional and physical challenges of living with warts and the various paths to successful treatment.
Success Stories
Profiles of people who have successfully treated their warts using different methods can inspire others to seek appropriate treatment. These stories can cover both medical treatments and home remedies.
Challenges Faced
Discussing the difficulties and setbacks in treating warts helps provide a realistic view of the process. This section can include common obstacles like recurring warts or ineffective treatments.
Expert Insights
Quotes from Dermatologists
Incorporating quotes from dermatologists and other medical professionals can add credibility and depth to the article. Experts can provide tips on identifying warts and recommend effective treatments.
Advice from Medical Professionals
Medical professionals can offer guidance on when to seek treatment, how to prevent warts, and what to expect from different treatment options. Their expertise can help readers make informed decisions.
Latest Research Findings
Highlighting recent research on HPV and warts can keep the article up-to-date and informative. This section can cover new treatment methods, advances in diagnosis, and findings on prevention.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Summarizing the main points helps reinforce the information covered in the article. Key points include the types of warts, their symptoms, causes, and various treatment options.
Importance of Seeking Medical Advice
Emphasizing the importance of consulting healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment ensures that readers understand the value of professional medical advice.
Encouragement for Further Education
Encouraging readers to continue learning about warts and HPV promotes better understanding and proactive health management. Providing links to reputable sources can facilitate further education.
Read Also:Unveiling PopAi’s AI Genius